What Is a Computer-Based System? Components & Applications
Modern workplaces rely on intricate digital networks to manage operations, yet few grasp their full scope. These frameworks blend hardware, software, and human oversight to process, store, and share critical information. Unlike basic tools like card catalogs, they operate as unified ecosystems designed for scalability and precision.
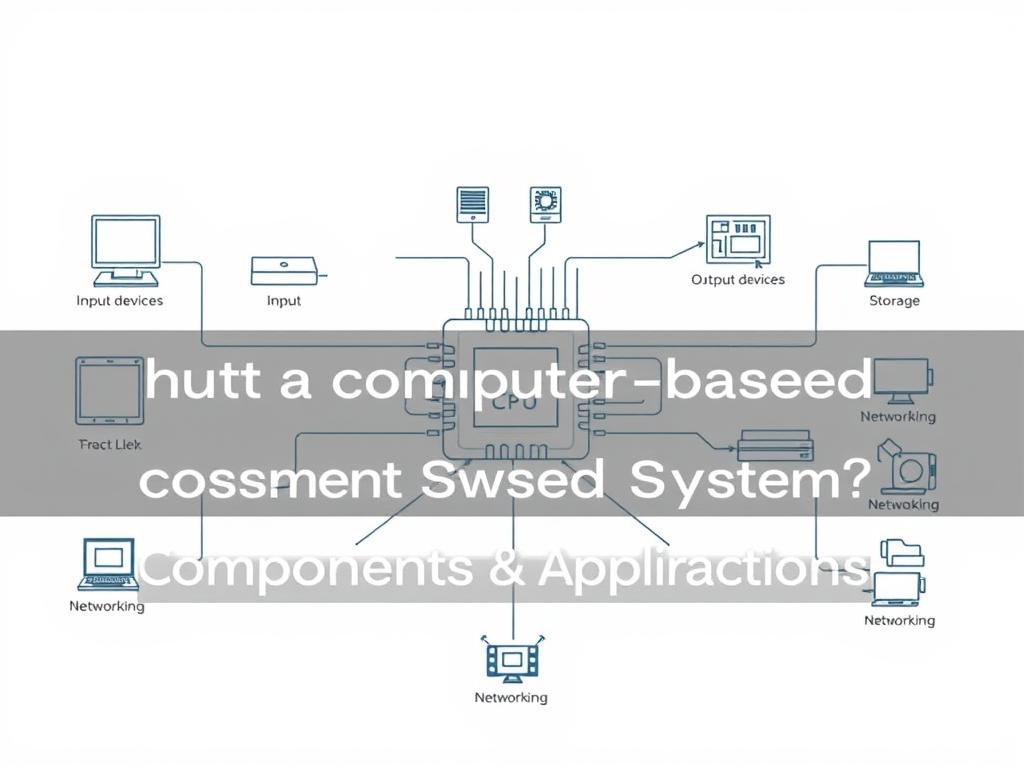
At their core, these architectures combine data collection tools, storage solutions, and processing power. Networks transmit details across departments, while indexing services ensure rapid retrieval. Human operators refine workflows, troubleshoot errors, and maintain security protocols—proving automation alone can’t sustain them.
From hospitals to financial institutions, information systems drive decision-making. They transform raw inputs into actionable insights, enabling tasks like inventory tracking or predictive analytics. Their evolution has shifted them from basic automation aids to indispensable operational backbones.
Key Takeaways
- Digital frameworks integrate hardware, software, and human oversight for seamless operations
- Data processing relies on interconnected components like storage, networks, and indexing tools
- Human intervention remains critical for system optimization and error management
- Modern enterprises use these structures for tasks ranging from basic record-keeping to advanced analytics
- Evolving beyond simple automation, they now serve as foundational business infrastructure
Fundamentals of Computer-Based Systems
Businesses thrive when their operational frameworks seamlessly integrate physical and digital resources. These architectures rely on five interdependent pillars: hardware, software, data, procedures, and human expertise. Each plays a distinct role in transforming raw inputs into strategic outputs.
Defining Modern Operational Frameworks
Contemporary workplaces use interconnected architectures to handle complex tasks. Physical devices like servers and sensors form the backbone, while coded instructions dictate their behavior. Together, they process facts into insights that drive daily decisions.
Essential Building Blocks
Hardware includes processors and storage drives that execute commands. Software acts as the brain, translating user needs into machine actions. Data becomes valuable when filtered through analytical tools, while documented procedures ensure consistency across teams.
Human operators remain irreplaceable despite automation. They configure settings, interpret results, and adapt workflows. A computer fundamentals tutorial demonstrates how these components interact in real-world scenarios.
From Punch Cards to Cloud Computing
Early systems required manual data entry and occupied entire rooms. Modern solutions leverage wireless networks and AI-powered analytics. This evolution highlights how advancements in processing power and storage capacity have revolutionized workplace efficiency.
Understanding What is a Computer Based System: Components & Management
Organizational success hinges on tailored information delivery across management tiers. Three distinct leadership levels require specialized digital frameworks to address unique operational needs and decision-making styles.

Key Components and Their Roles
Operational teams rely on real-time metrics like attendance logs and shift rotations. These structured datasets enable quick adjustments to daily workflows. Automated alerts and dashboards keep frontline supervisors informed about immediate priorities.
Mid-level leaders analyze quarterly sales breakdowns and production outputs. Tactical reports help allocate resources and optimize departmental performance. Interactive tools let managers test scenarios before implementing changes.
Executive decision-makers monitor market shifts through predictive analytics. Strategic dashboards highlight cost fluctuations and revenue patterns. This intelligence shapes long-term policies and organizational direction.
Integration of Processes and Technologies
Seamless data flow requires synchronized collection points and processing engines. Storage architectures must balance accessibility with security protocols. Network configurations adapt to handle varying data volumes across departments.
Developers bridge these elements using SQL for database optimization and Python for analytical models. JavaScript frameworks create intuitive interfaces for diverse user groups. Regular audits ensure components work cohesively as operational demands evolve.
Human expertise remains vital for interpreting complex outputs and refining automated workflows. This collaboration between technical systems and managerial insight drives continuous improvement across all organizational tiers.
Diverse Applications and Business Impacts
Advanced technological solutions transform how organizations operate across industries. Four core frameworks drive this evolution, each addressing specific operational needs while creating measurable value.
Enhancing Daily Operations with Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction Processing Systems automate repetitive tasks like order fulfillment and payroll management. They handle thousands of operations hourly while maintaining 99.9% accuracy rates. Retailers process payments faster than cashiers could manually, reducing customer wait times by 40%.
These systems eliminate manual data entry errors in billing and inventory tracking. Hospitals use them to manage patient admissions seamlessly, ensuring critical information flows between departments.
Decision Support and Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems convert sales figures into visual dashboards for executives. They identify trends like seasonal demand spikes, enabling proactive resource allocation. A regional chain might adjust staffing based on real-time foot traffic analytics.
Decision Support Systems tackle complex scenarios like supply chain disruptions. Managers simulate alternative vendor strategies before committing resources. Financial institutions use these tools to assess loan risks using dynamic credit score models.
Office Automation and the Future of Business Efficiency
Modern offices leverage integrated platforms combining email, document sharing, and project management. Cloud-based tools enable teams to collaborate across time zones while maintaining version control. Legal firms process contracts 60% faster using automated template systems.
Emerging technologies like blockchain document verification and AI-powered meeting schedulers redefine workplace productivity. These innovations reduce administrative workloads, allowing professionals to focus on strategic decision-making.
Conclusion
Digital ecosystems now form the backbone of enterprise success through seamless integration of technology and human expertise. These systems bridge technical precision with operational needs, transforming raw data into strategic assets across industries like healthcare and finance.
Modern architectures demand professionals skilled in both hardware optimization and workflow design. Their work ensures information systems evolve from basic automation to predictive tools that anticipate market shifts. Cloud platforms and blockchain integrations exemplify this relentless innovation.
Success hinges on balancing algorithmic efficiency with human judgment. While automated processes handle repetitive tasks, skilled analysts interpret patterns and refine outcomes. This synergy drives competitive advantage in sectors from retail inventory management to stock trading platforms.
As computer-based systems grow more interconnected, their role expands beyond operational support to shaping business models. Organizations prioritizing these frameworks gain agility in decision-making while maintaining robust security protocols. The future belongs to enterprises mastering this dynamic interplay between silicon and strategy.
FAQ
How do networks enhance computer-based system functionality?
Networks enable seamless communication between devices, allowing real-time data sharing across departments. Platforms like Cisco’s enterprise solutions optimize resource allocation, supporting collaborative workflows and centralized management.
What distinguishes decision support systems from transaction processing?
Decision support tools analyze historical and real-time data to guide strategic choices, while transaction systems handle routine tasks like sales orders. Microsoft Power BI exemplifies analytics-driven decision-making, unlike SAP’s transaction-focused ERP software.
How has cloud storage revolutionized data accessibility?
Cloud platforms like AWS and Google Cloud provide scalable storage, eliminating physical hardware limits. Teams access critical information remotely, accelerating processes like inventory tracking or customer relationship management.
Why are cybersecurity protocols vital for these systems?
With rising cyber threats, tools like firewalls and multi-factor authentication protect sensitive data. IBM’s QRadar actively monitors network vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
How do automation tools impact operational efficiency?
Robotic process automation (RPA) from UiPath reduces manual tasks in invoicing or payroll. This minimizes errors, speeds up workflows, and allows staff to focus on innovation-driven projects.
What role do APIs play in system integration?
APIs act as bridges between software applications, enabling platforms like Salesforce to sync with Oracle databases. This interoperability ensures unified reporting and eliminates data silos across teams.